
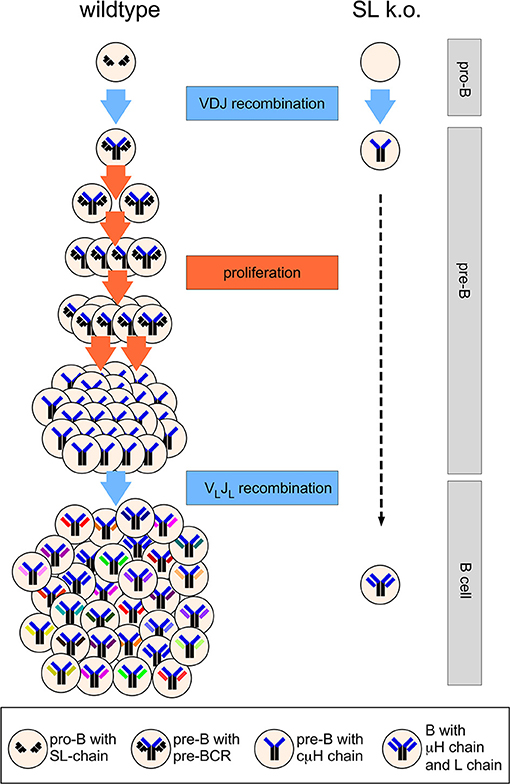
Successful sequential therapy with rituximab and belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a case series. Immunoglobulin heavy chain expression shapes the B cell receptor repertoire in human B cell development. Comparison of antibody repertoires produced by HIV-1 infection, other chronic and acute infections, and systemic autoimmune disease. Microbial exposures at the intestinal mucosa generated. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue harbours dominant B cell and plasma-cell clones associated with autoreactivity. We followed the development of the immunoglobulin repertoire in B cell populations, as well as single cells by deep sequencing. Self-reactive IgE exacerbates interferon responses associated with autoimmunity. IgA complexes in plasma and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis induce neutrophil extracellular traps via FcalphaRI. Objective To comparatively analyse the aberrant affinity maturation of the antinuclear and rheumatoid factor (RF) B cell repertoires in blood and tissues of. Analysis of the B cell receptor repertoire in six immune-mediated diseases. Mechanism and regulation of class switch recombination. B cell activation leads to rapid induction of extrafollicular and slower development of germinal center responses in draining lymph nodes after influenza infection As discussed above, respiratory tract-draining lymph nodes are the main site of influenza-induced B cell activation. Subsequent cellular interactions 1) permit the discriminant expansion of clones expressing relevant antibody molecules, 2) allow the active affinity alterations needed for effective ongoing immune responses, and 3) limit the potential deleterious effect of autoreactive cells.De Silva, N. B cell repertoirepopulation influences There are a number of peripheral development stages through which B cells can pass upon leaving the bone marrow. Further development of B cells occurs in the periphery in response to stimulation with the process of somatic hypermutation (SHM) through which point mutations are introduced in the genes coding for the V (D)J part of the immunoglobulin heavy (IgH) and light chain ( Jolly et al., 1996 ). Repertoire diversity is achieved centrally by somatic recombination of immunoglobulin (Ig) genes and peripherally by somatic hypermutation and Ig heavy chain class-switching. The B cell receptor (BCR) repertoire is highly diverse. The B-cell immunoglobulin receptor (BCR) is composed of two identical heavy chains (generated by recombination of V, D and J segments), and two identical light chains (generated by recombination of V and J segments). SARS-CoV-2 antigen (mixture of RBD and S proteins) positive BGCcells in lymph nodes from vaccinated mice were sorted by flow cytometry and then placed into the 10× Chromium (10× Genomics) for high-throughput single-cell V(D)J sequencing. Recent progress in categorizing the immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region genes into families as well as studies establishing their utilization in both fetal and adult life is helping to further refine these rules. Assessment of B Cell Repertoire in Humans. An overview of repertoire sequencing data production. Distinct BCR repertoires elicited by SARS-CoV-2 RBD and S vaccinations in mice. Many of the rules that regulate this phenomenon have been described, although the underlying enzymatic machinery responsible for these events remains to be elucidated. The well-studied genetic rearrangement that results in the juxtaposition of germ line-encoded variable, diversity, and joining elements remains the foundation for diversification on which the repertoire is built. This is made possible by molecular and cellular mechanisms uniquely suited to continuously generate a large number of individual receptor molecules and to select some for further expansion. The hallmark of the immune system is its ability to produce a seemingly infinite variety of antigen-binding receptors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
